A Java Class consists of a number of Methods. These methods help us in Code Reuse. These methods are similar to the Functions in C language. Let us know more about Java Method Signature, Naming convention and usage.
Note: All Java methods are written inside a Java Class.
Java Method Signature and Rules Explained
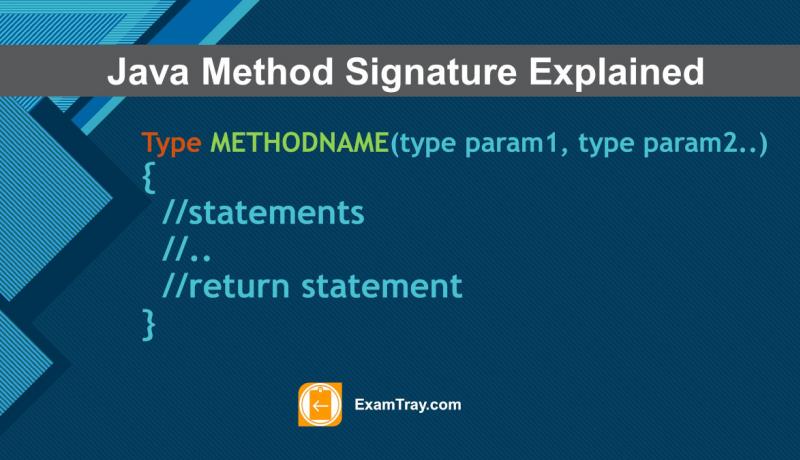
Java Method Signature is nothing but a combination of Return-Type, Method's Name and a Parameter list it accepts.
The method signature or syntax is as follows.
type METHODNAME(type param1, type param2..)
{
//statements
//..
//return statement
}
Let us know about parts of Java Method Signature.
- Return Type
- Method Name
- Parameter List
1. Return Type: A Java method may or may not return a value. If it returns nothing, we specify it explicitly mentioning a "void" before it. A method can return primitive or Object type values.
2. Method Name: A Java Method Name can be a combination of Alphabets, Numbers and Special Symbols (Underscore and Dollar only).
Java Method Naming Rules:
- Method name can start with a Letter or Alphabet.
- Method name can start with either Underscore(_) or Dollar($) symbol.
- Method name can not start with a number.
- Method name can contain numbers in-between or at the end.
- Method name can not be a keyword.
- Method name can be the same as the name of Class but it is not recommended.
3. Parameter List: Java methods can contain any number of parameters of any type. There can be zero parameters also. Variables which are part of a Parameter-list are also called Local Variables. Local variables are stored in Stack Memory. Also, the variables declared inside a method are also called Local Variables or Method Variables.
Naming Conventions or Rules for Local Variables:
- Name of a Local variable can start with an Alphabet lowercase or uppercase. Lowercase is preferred.
- Name of a Local variable can start with either an Underscore(_) or Dollar($) symbol.
- Name of a Local variable can not start with a number but it can contain numbers in-between or at the end.
- Name can not be a keyword.
- No two Local variables should have the same name.
- A Local variable can not be used without initializing if it is not part of the parameter list.
An example Java program below explains how to pass arguments to a Java method and return values or objects from a method.
class Table
{
int height;
}
public class JavaMethodExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
JavaMethodExample je = new JavaMethodExample();
Table t1 = new Table();
t1.height = 10;
je.show(t1); //Passing arguments to method
int changedValue = je.increase(t1);
System.out.println("New Height= " + changedValue);
//System.out.println("New Height= " + t1.height); //This code also works
}
void show(Table tab) //Receiving parameters in method
{
System.out.println("Height= " + tab.height);
}
int increase(Table tab) //Returning a value
{
tab.height = tab.height + 20;
return tab.height;
}
}
//OUTPUT
//Height= 10
//New Height= 30
In the above example, the method "show" receives parameters. The method "increase" receives an object reference as a parameter and returns an integer value back to the calling method. Remember that "main" is also a method which is the starting point of program execution.
This is how Java Methods are defined and used following Method Signature rules. Using a lower case first letter is a convention followed by good Java programmers.
Share this Last Minute Java Tutorial on Java Method Signature Rules with your friends and colleagues to encourage authors.
